Interferometry in Space
Our department plays the leading role in the development of the space-based gravitational-wave detector LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna). LISA technology also flies onboard the GRACE Follow-On mission, which observes climate change trough changes in the Earth's gravitational field. The department also was a major player in the LISA Pathfinder mission, which successfully tested key technologies for LISA from 2015 until 2017.
LISA will be a mission of discovery – the first gravitational-wave observatory in space. It will gather entirely new information about the dark, invisible Universe and work hand in hand with other astronomical observatories in the 2030s.
[more]
Satellite gravimetry measures the Earth's gravitational field from low Earth orbit. GRACE Follow-On uses LISA technology to monitor critical indicators of climate change caused by changes in the Earth's gravitational field. The mission uses a laser interferometer with nanometre accuracy between two satellites. Because of their expertise, researchers at the AEI are involved in the design of the laser interferometers for future similar missions.
[more]
LISA Pathfinder was the test mission of the European Space Agency ESA for LISA, the first gravitational wave observatory in space. LISA Pathfinder successfully demonstrated central LISA technologies.
[more]
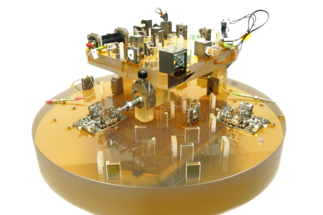
AEI is the largest laboratory worldwide for LISA interferometry. We cover the widest range of technologies while keeping close contact to all other participating groups.
[more]
by members of the “Space Interferometry” group
[more]