Interferometry on Earth
Currently, all existing gravitational-wave detectors are ground-based Michelson-type laser interferometers. The AEI is part of an international collaboration which runs the existing detectors: GEO600, the Virgo detector, both the LIGO detectors, KAGRA, and in the near future LIGO India. The AEI laboratories house various experiments in this area. The institute also develops design concepts for future ground-based dectectors such as the Einstein Telescope and tests new technologies using a detector prototype. In ALPS II, AEI laser technology is used for experimental particle physics.
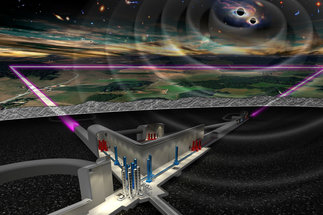
The Einstein Telescope (ET) is a design concept for a European third-generation gravitational-wave detector, which will be 10 times more sensitive than the current advanced instruments of the second generation.
[more]
GEO600 is a gravitational-wave detector and a key technology development center of the international gravitational-wave research community. Technologies developed and tested in the GEO project are now used in all large gravitational-wave detectors.
[more]
ALPS II (
Any Light Particle Search II) is looking for a new, light-weight, set of particles called axion-like-particles. These could explain dark matter and other phenomena that the standard model of particle physics cannot describe.
[more]
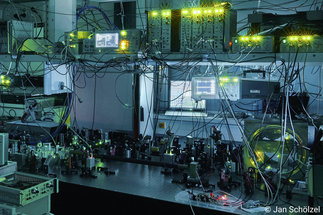
The AEI 10 meter prototype facility will host an ultra-low noise 10 m interferometer and serve as a test bed for new gravitational-wave detector technology.
[more]
The AEI has a long history in the design, fabrication and installation of lasers and squeezed light sources in ground based gravitational-wave interferometry.
[more]
The AEI is a partner in the aLIGO project and contributes the pre-stabilized laser system for all aLIGO detectors. Furthermore AEI scientists are involved in the commissioning and operation of the aLIGO interferometers.
[more]