Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA)
LISA, a space-based detector with million-kilometer long arms will detect low-frequency gravitational waves that cannot be measured by ground based gravitational wave detectors.
The LISA movie
LISA will be the first observatory in space to explore the “Gravitational Universe”. LISA will complement our knowledge about the beginning, evolution and structure of our universe.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aTPkoZxyovo
Images
Note: Publication of the images and the movie requires proper credits and written permission. Please contact the AEI press office in advance of publication or for higher-resolution versions.

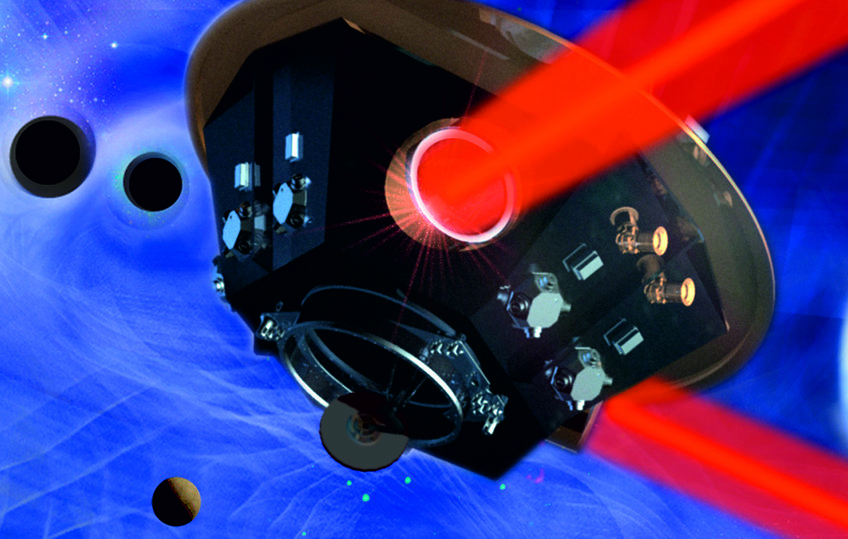
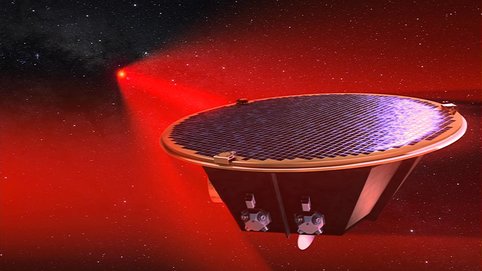
A LISA satellite: The LISA mission will detect gravitational waves in space using a trio of satellites, separated by millions of kilometers.
© Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Milde Marketing Science Communication, exozet

A LISA satellite: The LISA mission will detect gravitational waves in space using a trio of satellites, separated by millions of kilometers.
© Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Milde Marketing Science Communication, exozet. Simulation: C. Henze (NASA)

Artist's impression of a LISA spacecraft with a laser beam: The LISA mission consists of one “Mother” and two “Daughter” spacecraft orbiting the Sun in a triangular configuration. The three satellites are separated by a distance of 2.5 Mio km. The spacecraft are connected by laser beams forming the arms of a high precision laser interferometer. This interferometer senses gravitational waves by monitoring the changes in distance between free falling test masses inside the spacecraft.
© Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Milde Marketing Science Communication, exozet
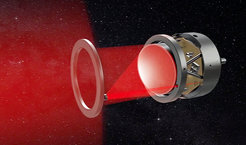
Artist's impression of an LISA instrument.
© Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Milde Marketing Science Communication, exozet

Artist's impression of the LISA mission satellites in the solar system observing gravitational waves from a distant galaxy.